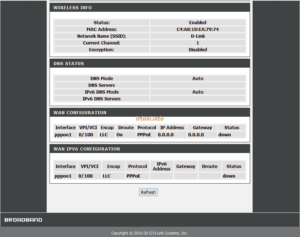
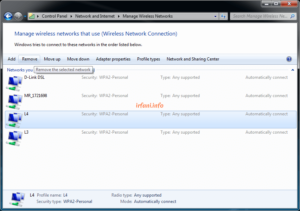
Internet Speed Test
Actually, I am confused to give the right title to this article, but I hope you can understand it from the explanation I gave. At this time, I will discuss the internet bandwidth that is not in accordance with what I should get from the ISP.
Previously, I had a similar article but it was not uploaded because the bandwidth at that time was only 10 Mbps, so it was not maximum for this discussion. For this reason, when I wanted to make this article, I looked for a higher bandwidth first and finally I was able to use the Up To 500 Mbps bandwidth for downloads and uploads. Why do I use the word Up To? just to make sure that later if there is a difference that is not far from 500 Mbps, I will not have a problem with it.
A few introductory paragraphs before I go to the main destination.
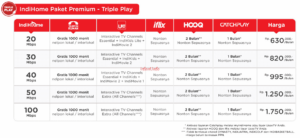
Here I take an example of an offer from an ISP:
Source https://indihome.co.id/tripleplay
Source https://my-republic.net/
Source https://cbn.id/personal/fiber/cbn-fiber.html
If you look at the 3 images above, then the highest speed offered by CBN, which is Up To 1 Gbps. Before I go any further, I emphasize that the testing here is about bandwidth speed, regardless of stability and other things.
The decision to take internet bandwidth services is generally adjusted to your needs, including:
- Internet usage
- The number of users
At point number 1, it is relative, whether it is used only for browsing, online games or work, because in general, a good salesperson will first ask the needs of his potential customers, so that they can give the right direction.
For point number 2, generally potential customers do not take this into account and will only complain if the connection is slow which has been unconsciously used by people around them at the same time. For example, I take a bandwidth of 10 Mbps, which if I use it myself is more than enough, but if my family/colleagues use it at that time, of course it will be reduced because the bandwidth is divided between them.
Actually, there is 1 additional point that is less often taken into account, namely devices used for internet connections, such as routers, access points (APs), switches and our own devices such as laptops and cellphones that are commonly used. If you connect a network device with different speeds, the connected device such as a PC, laptop or cellphone will be limited by that device.
Where is the influence? If you are taking a service below 50 Mbps, this can be ignored, but if you are using a service of 50 Mbps or above, this is worth taking into account.
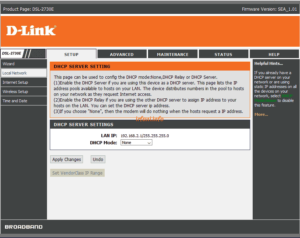
Topology, this is the most important point, because if you know this topology, it will make it easier in the checking process if there are problems. Make sure you pay attention or ask again when the internet installation process is in your place.
If your service already uses a Fiber connection, there will generally be media converters such as BDCOM, ONT and the like installed in your place that can function as an internet source or just media so there must be an additional router. The point is that ISPs will usually provide devices according to the services you use.
Example of one of the ONT devices
Before doing the experiment, I’ll explain the bandwidth and topology of the service I’m using.
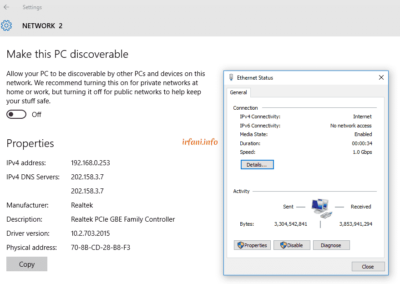
Bandwidth = Up To 500 Mbps
Connection type = Broadband
Topology = ISP <-> My device
<-> = cable LAN cat 5
As per the topology image above, the ISP only gives me an ethernet (LAN) cable to connect to my device, so the internet source will be my own device such as a router or laptop.
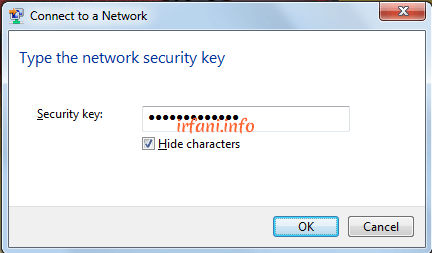
Is it clear enough to get here? Hopefully yes, hehehe.
Ok, I’ve done a simulation and here’s the result:
| Laptop | Processor / RAM | Port LAN | Lokal (Mbps) | Internasional (Mbps) | Kesimpulan | ||
| Download | Upload | Download | Upload | ||||
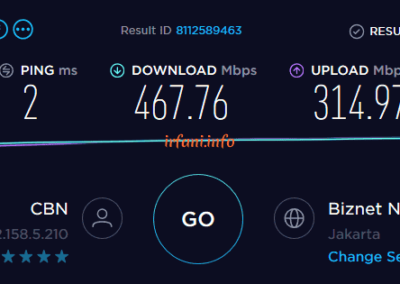
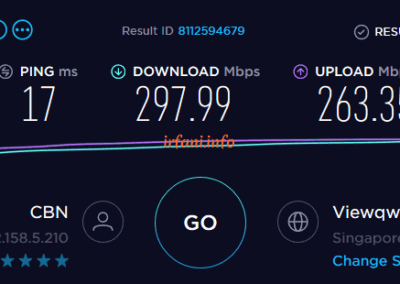
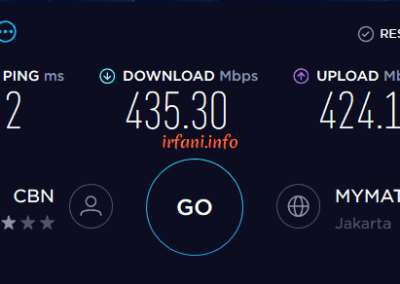
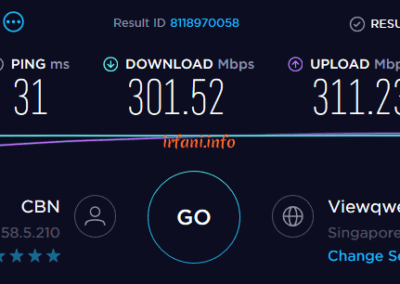
| HP 240 G6 | i5 7200U / 8 GB | Gigabit | 467 | 314 | 297 | 263 | OK |
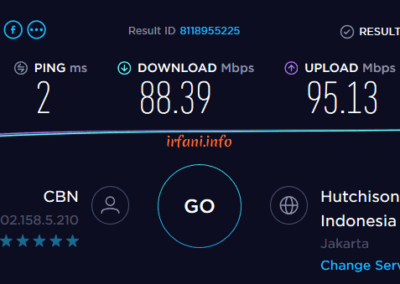
| HP 240 G6 | i5 7200U / 8 GB | USB Fast Ethernet | 88 | 95 | – | – | kendala di perangkat USB |
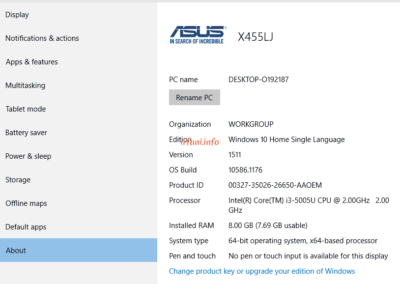
| Asus X455LJ | i3 5005U / 8 GB | Gigabit | 435 | 424 | – | – | OK |
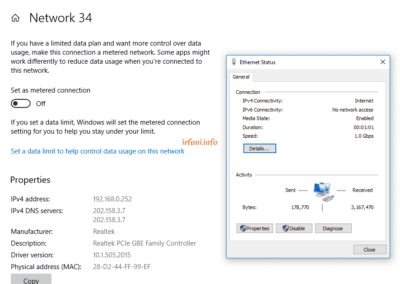
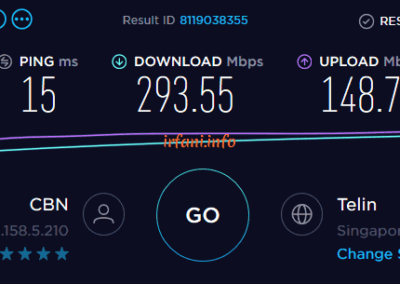
| Lenovo G40 | i5 5210U / 4 GB | Gigabit | 301 | 311 | 293 | 148 | kendala di RAM |
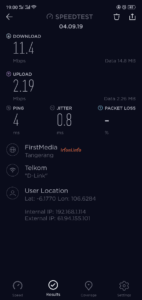
The results of the table above show that the bandwidth is close to 500 Mbps from a laptop that uses a Gigabit port and 8 GB of RAM, besides that it is still far from what is expected. For USB Fast Ethernet, I only use it as a comparison add-on, because on the HP 240 G6 there is only 1 ethernet port available. Oh yes, in this case I don’t really take into account uploads if they don’t fit because I think almost some internet users download more than uploads.
For international traffic, why didn’t it arrive too? Please remember, almost all ISPs that offer internet if they do not mention the bandwidth line, then it is certain that it is local bandwidth, why? because ISPs must pass the IIX line which incidentally is for use in Indonesia, while for international links (IX), they must have cooperation with other ISPs outside Indonesia (Upstream).
Remember, I adjusted to the title of this article, so I only did a speed test to make sure the internet speed I was using was appropriate. This is also a key point before finding any other issues that can be reported to the relevant ISP.
Hopefully by this point you can understand it first, because if you don’t understand it, it may be a bit difficult to understand the next article that will be related to many devices.
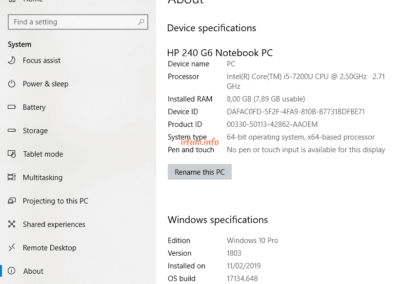
Test results with the HP 240 G6
Test results with Asus X455LJ
Test results with the Lenovo G40